TheEvolutionofJapan'sTelecomSector
Certainly! Here is a text that fits your requirements:
—
The evolution of Japan’s telecom sector has been a fascinating journey, marked by rapid advancements and significant transformations. Japan has long been recognized as a leader in technology and innovation, and its telecommunications industry is no exception. Over the years, this sector has undergone numerous changes to adapt to new technologies and meet the growing demands of consumers.
In the early days, Japan’s telecom industry was dominated by Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Public Corporation (NTT), which was a government monopoly. However, in 1985, the Japanese government decided to privatize NTT to encourage competition and foster innovation within the industry. This move paved the way for new players to enter the market, leading to increased competition and better services for consumers.
As mobile technology began to rise in popularity during the late 1990s and early 2000s, Japan quickly embraced these advancements. The country became one of the first in the world to roll out third-generation (3G) mobile networks on a large scale. This allowed Japanese consumers access to high-speed internet on their mobile devices well before many other countries.
The introduction of smartphones further revolutionized Japan’s telecom sector. Companies like NTT DoCoMo played pivotal roles by launching advanced mobile services that catered specifically to smartphone users. As consumer preferences shifted towards more data-centric services, Japanese telecom companies invested heavily in infrastructure upgrades such as fiber-optic networks.
Recently, there has been a growing interest in eSIM technology within Japan’s telecom industry. An eSIM is an embedded SIM card that allows users greater flexibility when switching carriers or plans without needing physical SIM cards. Although still emerging compared with traditional SIM cards, eSIM represents another step forward for Japan’s ever-evolving telecom sector.
In conclusion, Japan’s telecommunications industry continues adapting swiftly alongside technological innovations while maintaining its reputation as a global leader in adopting cutting-edge technologies efficiently and effectively.
UnderstandingeSIMTechnology

Certainly! Here is a brief article on the topic “Understanding eSIM Technology” in English:
—
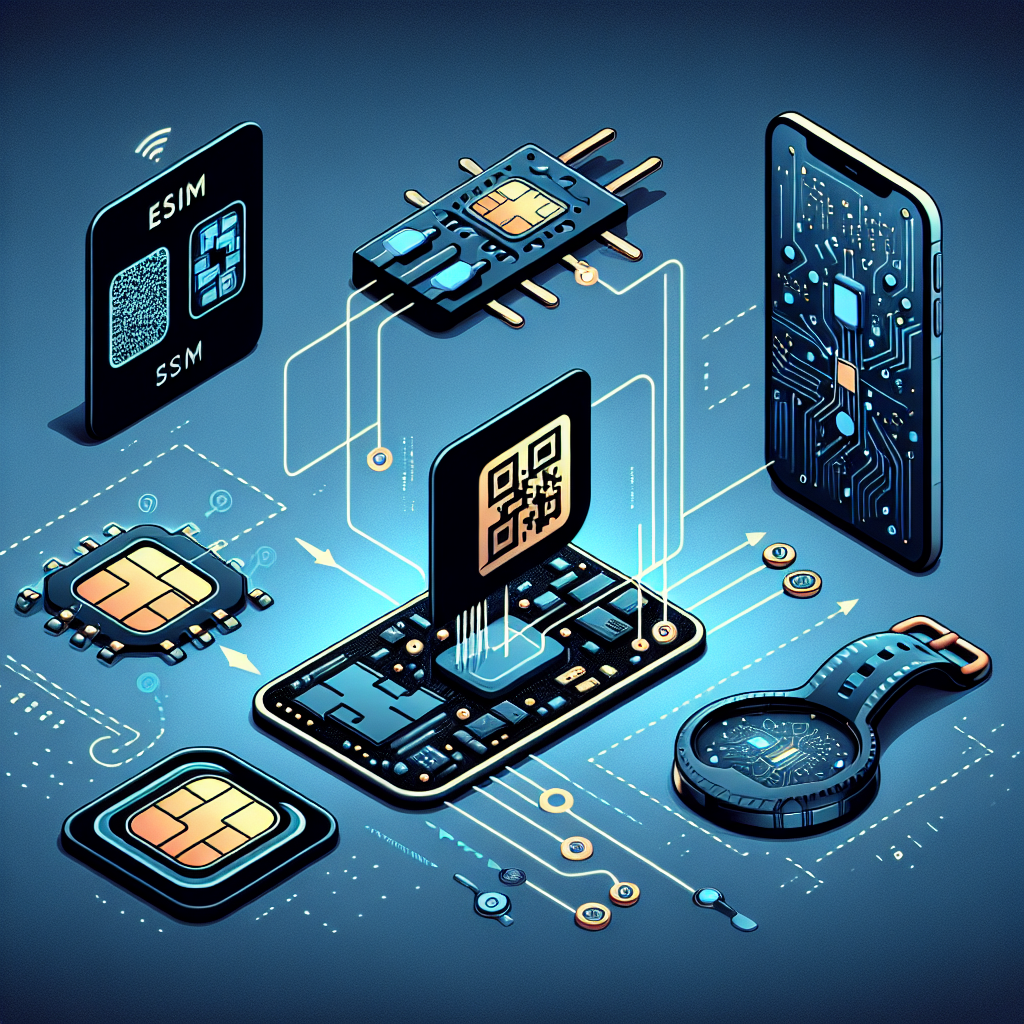
eSIM technology, short for embedded SIM, is revolutionizing the way we connect our devices to mobile networks. Unlike traditional SIM cards, which are physical cards inserted into a device, eSIMs are embedded directly into the device’s hardware. This means that users no longer need to physically switch SIM cards when changing carriers or plans.
The eSIM operates through remote provisioning. This allows consumers to download carrier profiles and manage multiple subscriptions directly from their devices without needing to visit a store or wait for a physical card to arrive in the mail. As such, it offers greater flexibility and convenience for users.
In Japan, where technological innovation is highly valued, understanding eSIM technology is crucial as it represents a significant shift in how telecom services can be accessed and managed. For consumers who travel frequently or use multiple devices, eSIM provides an efficient solution by allowing them to switch between different network providers seamlessly.
Moreover, eSIM technology supports more compact device designs since there’s no need for a physical slot dedicated to holding a traditional SIM card. This can lead to slimmer smartphones and more space for other components like larger batteries or advanced sensors.
However, not all devices currently support eSIM technology. It requires compatible hardware and software capabilities that are still being rolled out across new models of smartphones and other connected gadgets.
For Japanese consumers looking forward to adopting this technology, it’s important they ensure their devices support eSIM functionality before making any changes with their network providers. Familiarity with how remote provisioning works will also help them take full advantage of what this technology has to offer.
Overall, understanding how eSIM works opens up new possibilities in personal connectivity management and marks an exciting development in Japan’s telecom industry landscape. As more carriers adopt this standard globally and locally within Japan itself, users can expect even greater flexibility and control over their mobile services in the near future.
KeyPlayersinJapan’seSIMMarket

Certainly! Here is a paragraph about “Key Players in Japan’s eSIM Market” written in a polite and informative tone:
—
In Japan’s rapidly evolving telecom industry, several key players are driving the adoption and implementation of eSIM technology. Among these, NTT Docomo, KDDI (au), and SoftBank stand out as the primary mobile network operators that have embraced eSIM capabilities. These companies have been at the forefront of integrating this innovative technology into their service offerings to provide enhanced flexibility and convenience to their customers.
NTT Docomo, being one of the largest telecom providers in Japan, has taken significant steps towards promoting eSIM usage among its subscribers. They offer a variety of plans that support eSIM functionality, which allows users to switch between different carriers without needing to physically change SIM cards. This move aligns with their commitment to providing cutting-edge solutions that cater to the modern consumer’s needs.
Similarly, KDDI (au) has been proactive in incorporating eSIM technology into its services. By offering seamless activation processes and robust customer support for eSIM users, KDDI ensures that consumers can easily transition from traditional SIM cards to this more advanced option. Their efforts reflect an understanding of global trends and a desire to stay competitive in an increasingly digital landscape.
SoftBank also plays a critical role in advancing eSIM adoption within Japan. Known for its innovation-driven approach, SoftBank provides comprehensive support for devices equipped with eSIM capabilities. They focus on creating user-friendly experiences that simplify connectivity changes and enhance overall satisfaction for tech-savvy individuals who prioritize flexibility.
In addition to these major players, emerging virtual network operators (MVNOs) are beginning to explore opportunities within the eSIM market as well. By leveraging partnerships with established carriers or developing independent solutions, these smaller entities contribute to diversifying options available for Japanese consumers interested in adopting this new technology.
Overall, through collaborative efforts among leading telecom companies and innovative newcomers alike, Japan’s eSIM market continues to grow steadily—offering promising prospects for both providers and consumers seeking modern connectivity solutions.
—
BenefitsofeSIMforJapaneseConsumers

Certainly! Here is a text in a polite form about the benefits of eSIM for Japanese consumers:
—
The introduction of eSIM technology offers numerous benefits to Japanese consumers. Firstly, eSIM allows for greater convenience and flexibility. Unlike traditional SIM cards that require physical swapping when changing carriers or traveling internationally, eSIM can be easily reprogrammed remotely. This means that consumers can switch between different mobile network operators without needing to visit a store or wait for a new SIM card to arrive by mail.
Moreover, eSIM technology is particularly advantageous for frequent travelers. With an eSIM-enabled device, Japanese consumers can seamlessly connect to local networks abroad without incurring high roaming charges. They can simply download a local carrier’s profile onto their device and enjoy local rates, making international travel more affordable and hassle-free.
Another benefit is the potential cost savings associated with using eSIMs. Consumers have the opportunity to compare and select from various mobile plans available on the market with ease, ensuring they choose the most cost-effective option that suits their needs. This competition among carriers may lead to more attractive pricing and better service offerings.
In addition to economic advantages, eSIM contributes positively towards environmental sustainability by reducing plastic waste associated with traditional SIM cards. As environmental concerns become increasingly important in Japan, adopting technologies like eSIM aligns with efforts towards creating a more sustainable society.
Lastly, devices equipped with an embedded SIM tend to have enhanced security features. Since there is no physical card that can be removed or lost, there is less risk of unauthorized access or theft of personal information stored on the SIM card.
Overall, while transitioning fully to this new technology may take time due to existing infrastructure and consumer habits, the benefits that eSIM brings are clear and compelling for Japanese consumers looking for convenience, cost savings, sustainability, and security in their mobile telecommunications experience.
—
ChallengesFacingeSIMAdoptioninJapan

Certainly! Here is a text on the topic “Challenges Facing eSIM Adoption in Japan” written in a formal style:
—
The adoption of eSIM technology in Japan’s telecom industry does face several challenges that need to be addressed for its widespread acceptance. One of the primary challenges is the lack of awareness and understanding among consumers about eSIM technology. Many Japanese consumers are still unfamiliar with how eSIMs work and the potential benefits they offer over traditional SIM cards. This lack of knowledge can lead to hesitation in adopting new technology, as people tend to stick with what they know.
Additionally, there are technical challenges associated with integrating eSIM technology into existing infrastructure. Telecom operators need to invest in upgrading their systems to support eSIM functionality, which can be both time-consuming and costly. Smaller telecom companies may find it particularly challenging to allocate resources for such upgrades, potentially limiting their ability to offer competitive services.
Regulatory hurdles also pose a significant challenge for eSIM adoption in Japan. The country has strict regulations concerning telecommunications and consumer privacy, which can complicate the implementation process for new technologies like eSIMs. Ensuring compliance with these regulations while rolling out new services requires careful planning and collaboration between telecom operators and regulatory bodies.
Moreover, there is resistance from some stakeholders within the industry who have vested interests in maintaining the status quo with physical SIM cards. These stakeholders may include manufacturers of traditional SIM cards or businesses that rely on physical distribution channels for their products.
Finally, consumer behavior plays a crucial role in determining how quickly eSIM adoption takes off. Japanese consumers tend to be brand loyal and may prefer sticking with established service providers rather than exploring new options enabled by eSIM flexibility unless incentivized through attractive offers or promotions.
In conclusion, while there are several challenges facing the adoption of eSIM technology in Japan, addressing these issues through education, investment in infrastructure upgrades, regulatory cooperation, and strategic marketing efforts will be key steps towards realizing its full potential within the Japanese telecom sector.
FutureProspectsforeSIMinJapan

Certainly! Here is a text on the future prospects of eSIM in Japan, written in English with a formal tone:
—
The future prospects for eSIM technology in Japan appear promising as the nation continues to embrace digital innovation. As more consumers and businesses understand the benefits of eSIM, its adoption is expected to grow significantly. The Japanese government has been supportive of technological advancements and may play a crucial role in facilitating the widespread use of eSIM by establishing favorable regulations and standards.
One of the main drivers for eSIM adoption in Japan will be its integration into various consumer electronics beyond smartphones, such as tablets, laptops, smartwatches, and IoT devices. This expansion will likely encourage telecom providers to enhance their infrastructure and offer more competitive plans tailored specifically for eSIM users.
Moreover, Japanese consumers are known for their appreciation of cutting-edge technology. As awareness about the convenience and flexibility offered by eSIM increases, it is anticipated that demand will rise accordingly. This shift could lead telecom operators to prioritize eSIM services within their offerings.
However, successful widespread adoption will depend on overcoming certain challenges such as ensuring compatibility across different devices and networks. Collaboration among device manufacturers, telecom operators, and regulatory bodies will be essential to address these issues effectively.
Furthermore, as global travel resumes post-pandemic, international travelers visiting Japan might prefer using eSIM for seamless connectivity without needing physical SIM cards. This trend could boost tourism-related communication services and provide additional revenue streams for local telecom companies.
In conclusion, while there are challenges ahead in terms of technical standardization and market education efforts required from stakeholders involved—telecom companies remain optimistic about integrating this innovative solution into everyday life seamlessly over time due largely thanks due diligence shown thus far towards embracing new technologies like never before seen within industry history itself!





